Description:
The Grumman
F-14 Tomcat is a supersonic, twin engine, variable sweep wing, two-place
strike fighter. The Tomcat's primary missions are air superiority, fleet
air defense, and precision strike against ground targets. My
experiences with the F-14 began in 1983, when I was assigned to VF-124,
Miramar California ("Fightertown USA"). I served as an
avionics technician, later became a supervisor, and then later became an
instructor for west coast F-14 squadrons, avionics systems. As a
Naval Officer, I was responsible for avionics support for two embarked
F-14 squadrons aboard USS Carl Vinson.
[Back
To Top]
Background:
The F-14
entered the fleet in 1973, replacing the F-4 Phantom II. The
F-14B, introduced in November 1987, incorporated new General Electric
F-110 engines. In 1995, an upgrade program was initiated to
incorporate new digital avionics and weapon system improvements to
strengthen its multi-mission competitive edge. The F-14D, delivered in
1990, was a major upgrade with F-110 engines, new APG-71 radar system,
Airborne Self Protection Jammer (ASPJ), Joint Tactical Indicator
Distribution System (JTIDS) and Infrared Search an Track (IRST).
Additionally, all F-14 variants were given precision strike capability
using the LANTIRN targeting system, night vision compatibility, new
defensive countermeasures systems and a new digital flight control system.
Boasting up
to six AIM-54C Phoenix AAMs, the F-14A is capable of destroying six
separate targets at ranges in excess of 100 miles. After problems
with the initial TF30 engine, Grumman produced a Tomcat powered by a pair
of GE-400 turbofans. The aircraft became the prototype for the
F-14A+, or later the production F-14B. A vastly improved model, the
F-14D Super Tomcat, of which 37 were built, first took to the air on
February 9, 1980 and includes enhanced radar and cockpit, a dual IRST/TV
under-nose pod, and increased AAM capability. Tomcats are now being
equipped for night-attack bombing duty with the use of Low Altitude
Navigation and Targeting Infrared for Night (LANTIRN) pods. Placed on an
external point beneath the right wing, the LANTIRN pod will allow the F-14
to drop laser-guided bombs under the cover of darkness.
The wings
have the ability to automatically sweep during flight,
with a manual override provided. The twin, swept fin-and-rudder vertical
surfaces are mounted on the engine housings and canted outward. Normal sweep range is 20 to 68 deg with a 75-deg "over-sweep"
position provided for shipboard hangar stowage; sweep speed is 7.5 deg per
second.
For roll
control below 57 deg, the F-14 uses spoilers located along the upper wing
near the trailing edge in conjunction with its all-moving, swept
horizontal stabilizers, which are operated differentially; above 57-deg sweep, the
horizontal stabilizers operate alone. For un-swept, low-speed combat maneuvering, the
outer 2 sections of trailing edge flaps can be deployed at 10 deg and the
nearly full-span leading-edge slats are drooped to 8.5 deg. At speeds
above Mach 1.0, glove vanes in the leading edge of the fixed portion of
the wing extend to move the aerodynamic center forward and reduce loads on
the horizontal stabilizers.
The engine intakes have 2 variable-angle ramps, a
bypass door in the intake roof, and a fixed ramp forward; exhaust nozzles
are mechanically variable. Viewed from the front, the top of the intakes are
tilted toward the aircraft centerline; from above, the engines are canted
outward slightly to reduce interference between intake airflow and the
fuselage boundary layer. The engines exhaust through mechanically
variable, convergent-divergent nozzles.
The AWG-9
is a pulse-Doppler, multi-mode radar with a designed capability to track
24 targets at the same time while simultaneously devising and executing
fire control solutions for 6 targets. The cockpit is fitted with a Kaiser
AN/AVG-12 Head-Up Display (HUD) co-located with an AN/AVA-12 vertical
situation display and a horizontal situation display. A chin mounted
Northrop AN/AXX-1 Television Camera Set (TCS) is used for visual target
identification at long ranges. Electronic Support Measures (ESM) equipment
include the Litton AN/ALR-45 radar warning and control system, the
Magnavox AN/ALR-50 radar warning receiver, Tracor AN/ALE-29/-39
chaff/flare dispensers (fitted in the rear fuselage between the fins), and
Sanders AN/ALQ-126 deception jamming system.
The F-14
has visual and all-weather attack capability to deliver Phoenix and
Sparrow missiles, as well as the M-61A1 Vulcan cannon, and Sidewinder missiles for close
in air-to-air combat. The F-14 also has the LANTIRN targeting system that
allows delivery of various laser-guided bombs for precision strikes in
air-to-ground combat missions. The F-14, equipped with Tactical Air
Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS) is the Navy's only manned tactical
reconnaissance platform.
The Tomcat
has an internal 20-mm Vulcan Gattling-type gun fitted on the left side,
and can carry Phoenix, Sparrow, and Sidewinder AAMs. Up to 6 Phoenix
missiles can be carried on 4 fuselage stations between the engines and on
2 pylons fitted on the fixed portion of the wing; 2 Sidewinder AAM can be
carried on the wing pylons above the Phoenix mount. Although the F-14 was
tested with conventional "iron" bombs on its external hard
points in the 1960s, the BRU-10 ejection racks were not strong enough to
provide a clean separation. Tests in 1988-1990 showed that BRU-32 racks
could drop Mk 80-series bombs safely. Later tests would qualify the AGM-88
HARM and the AGM-84 Harpoon.
Since the
early 1980s F-14s have had provision for the attachment of the Tactical
Air Reconnaissance Pod System (TARPS), carrying optical and infrared
cameras and permitting the aircraft to perform the photo reconnaissance
role without degrading its performance in other roles. The only
modifications required are fuselage wiring changes and the addition of cockpit
TARPS control boxes.
[Back
To Top]
Design:
The F-14
has a wing able to take any angle automatically between 20 to 68 degrees
according to the varying demands of the mission , it actually usage has
been almost totally in the fighter/interceptor role. The main advantages
of the swing wing for the F-14 includes to reduce take off and landing
speed , facilitating cat ( accelerated ) launches at high gross weight and
to reduce fuel consumption in subsonic loiter and enable higher altitude
to be reached at low subsonic speeds.
Although
the Tomcat and the Grumman A-6 Intruder are more different in other ways,
both planes share a similar inlet duct, wing, and landing gear
geometry. Unlike the A-6 the long fully augmented engines
extend far down stream to variable nozzles at the extreme rear of the
aircraft , widely separated throughout by fuselage fuel tanks, a
canted vertical tail above each engine, and the airbrake above and below
the wide gap between the nozzles.
The pilot
and RIO sit well separated in a capacious tandem cockpit. Aerodynamics of the F-14
Tomcat are complex with a large fixed wing glove
carrying the outer wing pivot 17ft and 10 inches apart and incorporating
retractable canards .
[Back
To Top]
Avionics:
The Tomcat
is believed to have been the world first fighter to have a look down and
shoot down capability. This capability was the last major gap to be
closed in air defense. It is also claimed that the Tomcat not only
has capability against hostile aircraft but also against sea skimming anti-ship
missiles.
AWG-9 radar
is a large ( 1,293 lb./586.5 kg ; 28 cu ft/0.79m cube) liquid cooled
package with the vital coherent pulse Doppler mode for look down
capability. The Tomcat was also the first fighter to have a track
while scan (TWS) radar, enabling the Tomcat to have a target range of over 100 miles (
160 km) to detect, select, and track up to 20 targets. This allows
it to pick out the 6
most threatening targets and launch phoenix missiles against them. Each
phoenix is coded with its own target . With the help of Northrop TV
Camera Set (TCS), the task of long range recognition is greatly assisted.
One of the
problems involving the use of the AIM-7 AAM was that the Tomcat needs to
constantly flying toward the hostile fighter to provide target
illumination for the missile
Kaiser
provided the AN/AVG-12 vertical display indicator group (VDIG) situation display and electronically
separated but mechanically integrated HUD. The HUD simply uses the inside
face of the wind screen instead of the typical combining glass assembly.
Other
systems
included in the F-14 are an expandable memory digital computer, laser gyro
INS (being retrofitted when funds permit) , Westinghouse/ITT ASPJ and
Hughes ITT JTIDS combined with the ITEK ALR 67 threat warning system .
Some Tomcats
have been fitted to carry the Tactical Air Recon POD system (TARPS) photo
and IR camera system.

F-14D Front Cockpit |
 |

F-14D Rear Cockpit |


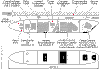


More
About F-14 TARPS
See
F-14 TARPS Images
[Back
To Top]
Power
Plant F-14B/D:
Two General
Electric F-110-GE-400 turbo fans rated at 71.56 kN and 120.1 kN with
afterburn . Garret ATS 200-50 air turbine starter. The F110 engine has 43 %
more reheated thrust and 37% more military thrust (no after-burn) than the
TF-20-P-414A in F-14A, resulting in 20% more specific excess energy and 30%
lower fuel consumption. The engines also have 62% greater launch deck
intercept radius and 34 % more combat air patrol time. Total fuel
capacity is 9,029l liters plus 2 external tank each capable of carrying
1,011 liters.

[Back
To Top]
Technical
Information:
|
Prime
contractor |
Grumman Aerospace Corporation |
|
Function |
Carrier-based multi-role strike
fighter |
|
Crew |
Two: pilot and radar intercept
officer |
|
Unit Cost |
$38 million |
|
In-service
year |
F-14A - 1974, F-14D - 1980 |
|
Length |
61 feet, 9 inches (18.6 meters) |
|
Height |
16 feet (4.8 meters) |
|
Wing span
extended (68 degrees) |
64 feet, 2 inches (19.5 m) |
|
Wing span
swept (20 degrees) |
38 feet, 3 inches (11.7 m) |
|
Max Wing
Loading |
642.5kg/m square |
|
Weight empty |
39,762 lbs. (18,036 kg) |
|
Max Fuel
(useable) |
7,348kg |
|
Max Take Off
Weight |
73,348 lbs. (33,724 kg) |
|
Speed |
2,500 km/h / 1,563 mph at ceiling |
|
Carrier
Approach |
125 knots |
|
Landing run
(field) |
732 meters |
|
Range |
2,013 miles ferry range (1,740
nautical miles) |
|
Ceiling |
56,000 ft |
|
Propulsion |
F-14A: Two Pratt & Whitney
TF-30P-414A turbofan engine with afterburners.
F-14B and F-14D: Two General Electric F110-GE-400 turbofan engines
with afterburners.
|
|
Thrust |
TF-30P-414A: 20,900 pounds (9,405
kg) static thrust per engine
F110-GE-400: 27,000 pounds (12,150 kg) static thrust per engine |
|
Max Power
Loading |
140.4kg/kN |
|
Armament |
Up to 13,000 pounds: One M61A1
20-mm Vulcan multi-barrel cannon with 675 rounds and a combination
of AIM-54 Phoenix, AIM-9 Sidewinder and AIM-7 Sparrow
missile, cluster bombs, and two drop tanks. |
Acknowledgement: Information on this page obtained from the
Military
Analysis Network.
More
Drawings & Photos:
Click Drawings and Photos
for Larger View





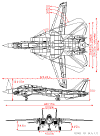

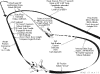


[Back
To Top]
|

